Exceptions
Note:
Internal PHP functions mainly use Error reporting, only modern Object oriented extensions use exceptions. However, errors can be simply translated to exceptions with ErrorException.
Source http://www.w3schools.com/php/php_form_url_email.asp
Using
die() function:
Defining
Custom Error Handling Function:
Syntax
Possible
Error levels
Exceptions
Handling:
Example:
Creating
Custom Exception Handler:
Example:
how to redirect all the not found pages in to a common page using htaccess
Go to command prompt, cd to the appropriate folder and type:
notepad .htaccess After confirmation dialog the file will be created and you will be editing it directly. If you just want to create an empty file, try
echo. > .htaccessorcreate the file by typing ".htaccess." in explorer, and the last dot will be removed automatically.
Exception::getCode — Gets the Exception code
This document will explain how to create a .htaccess file to redirect your site or site content. This will not redirect any emails for your domains.
1. Create an empty text file using a text editor such as notepad, and save it as htaccess.txt.
301 (Permanent) Redirect: Point an entire site to a different URL on a permanent basis. This is the most common type of redirect and is useful in most situations. In this example, we are redirecting to the "mt-example.com" domain:
The Code
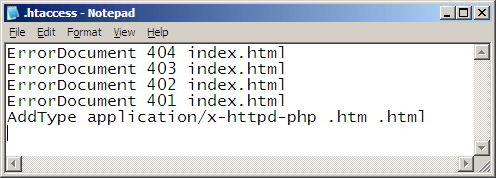
ErrorDocument 400 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 403 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 404 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 405 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 408 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 500 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 502 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 504 /errors.php
The PHP
=======================================================================
http://www.php.net/manual/en/language.exceptions.php
http://papermashup.com/create-an-error-page-to-handle-all-errors-with-php/
http://kb.mediatemple.net/questions/242/How+do+I+redirect+my+site+using+a+.htaccess+file%3F
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1918624/php-try-and-catch-for-sql-insert
Learn
PHP MySQL from ITClassSL@gmail.com Call +94 777 33 7279 Skype ITClassSL
PHP 5 has an
exception model similar to that of other programming languages. An exception
can be thrown, and caught
("catched") within
PHP. Code may be surrounded in a try
block, to facilitate the catching of potential exceptions. Each try must have at least one corresponding
catch block. Multiple catch blocks can be used to catch
different classes of exceptions. Normal execution (when no exception is thrown
within the try block, or when a catch matching the thrown
exception's class is not present) will continue after that last catch block defined in sequence.
Exceptions can be thrown (or re-thrown)
within a catch block.
When an
exception is thrown, code following the statement will not be executed, and PHP
will attempt to find the first matching catch
block. If an exception is not caught, a PHP Fatal Error will be issued with an
"Uncaught Exception ..."
message, unless a handler has been defined with set_exception_handler().
In PHP 5.5
and later, a finally block may
also be specified after the catch
blocks. Code within the finally
block will always be executed after the try
and catch blocks, regardless of
whether an exception has been thrown, and before normal execution resumes.
The thrown
object must be an instance of the Exception class or
a subclass of Exception.
Trying to throw an object that is not will result in a PHP Fatal Error. Note:
Internal PHP functions mainly use Error reporting, only modern Object oriented extensions use exceptions. However, errors can be simply translated to exceptions with ErrorException.
Tip
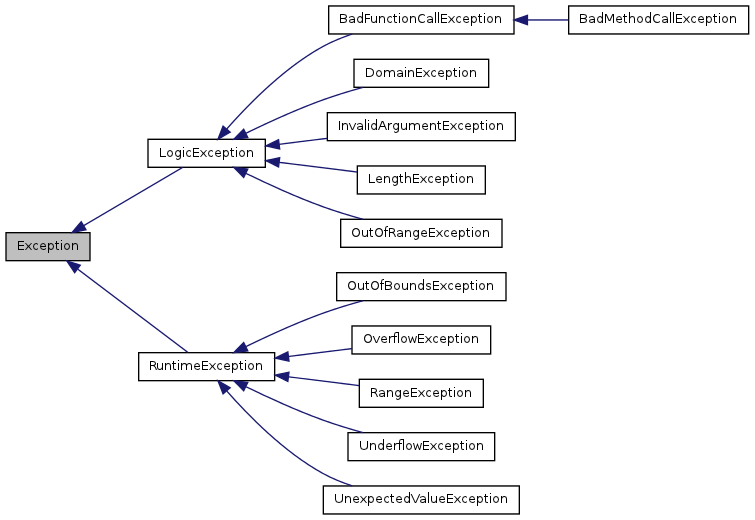
The Standard PHP Library (SPL)
provides a good number of built-in exceptions.- BadFunctionCallException
- BadMethodCallException
- DomainException
- InvalidArgumentException
- LengthException
- LogicException
- OutOfBoundsException
- OutOfRangeException
- OverflowException
- RangeException
- RuntimeException
- UnderflowException
- UnexpectedValueException
SPL provides a set of
standard Exceptions.
See also the Predefined
ExceptionsPHP - Validate Name, E-mail, and URL
php string validation preg_match Now, the script looks like this:
Example
<?php
// define variables and set to empty values
$nameErr = $emailErr = $genderErr = $websiteErr = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameErr = "Name is required";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
// check if name only contains letters and whitespace
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name)) {
$nameErr = "Only letters and white space allowed";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailErr = "Email is required";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
// check if e-mail address is well-formed
if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) {
$emailErr = "Invalid email format";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["website"])) {
$website = "";
} else {
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
// check if URL address syntax is valid (this regular expression also allows dashes in the URL)
if (!preg_match("/\b(?:(?:https?|ftp):\/\/|www\.)[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%?=~_|!:,.;]*[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%=~_|]/i",$website)) {
$websiteErr = "Invalid URL";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$comment = "";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderErr = "Gender is required";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
?>
// define variables and set to empty values
$nameErr = $emailErr = $genderErr = $websiteErr = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameErr = "Name is required";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
// check if name only contains letters and whitespace
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name)) {
$nameErr = "Only letters and white space allowed";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailErr = "Email is required";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
// check if e-mail address is well-formed
if (!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL)) {
$emailErr = "Invalid email format";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["website"])) {
$website = "";
} else {
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
// check if URL address syntax is valid (this regular expression also allows dashes in the URL)
if (!preg_match("/\b(?:(?:https?|ftp):\/\/|www\.)[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%?=~_|!:,.;]*[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%=~_|]/i",$website)) {
$websiteErr = "Invalid URL";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$comment = "";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderErr = "Gender is required";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
?>
Syntax
int preg_match (string pattern, string string [, array pattern_array],
[, int $flags [, int $offset]]]);
The preg_match() function searches string for pattern, returning true if pattern exists, and false otherwise.
Using
die() function:
While wirting your PHP program you should check all
possible error condition before going ahead and take appropriate action when
required.
Try following example without having /tmp/test.xt
file and with this file.
<?php
if(!file_exists("/tmp/test.txt"))
{
die("File not found");
}
else
{
$file=fopen("/tmp/test.txt","r");
print "Opend file sucessfully";
}
// Test of the code here.
?>
|
This way you can write an efficient code. Using abive
technique you can stop your program whenever it errors out and display more
meaningful and user friendly meassage.
Defining
Custom Error Handling Function:
You can write your own function to handling any error.
PHP provides you a framwork to define error handling function.
This function must be able to handle a minimum of two
parameters (error level and error message) but can accept up to five parameters
(optionally: file, line-number, and the error context):
Syntax
error_function(error_level,error_message,
error_file,error_line,error_context);
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
error_level
|
Required - Specifies the error report level for the
user-defined error. Must be a value number.
|
error_message
|
Required - Specifies the error message for the
user-defined error
|
error_file
|
Optional - Specifies the filename in which the error
occurred
|
error_line
|
Optional - Specifies the line number in which the
error occurred
|
error_context
|
Optional - Specifies an array containing every
variable and their values in use when the error occurred
|
Possible
Error levels
These error report levels are the different types of
error the user-defined error handler can be used for. These values cab used in
combination using | operator
Value
|
Constant
|
Description
|
1
|
E_ERROR
|
Fatal run-time errors. Execution of the script is
halted
|
2
|
E_WARNING
|
Non-fatal run-time errors. Execution of the script is
not halted
|
4
|
E_PARSE
|
Compile-time parse errors. Parse errors should only be
generated by the parser.
|
8
|
E_NOTICE
|
Run-time notices. The script found something that
might be an error, but could also happen when running a script normally
|
16
|
E_CORE_ERROR
|
Fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup.
|
32
|
E_CORE_WARNING
|
Non-fatal run-time errors. This occurs during PHP's
initial startup.
|
256
|
E_USER_ERROR
|
Fatal user-generated error. This is like an E_ERROR
set by the programmer using the PHP function trigger_error()
|
512
|
E_USER_WARNING
|
Non-fatal user-generated warning. This is like an
E_WARNING set by the programmer using the PHP function trigger_error()
|
1024
|
E_USER_NOTICE
|
User-generated notice. This is like an E_NOTICE set by
the programmer using the PHP function trigger_error()
|
2048
|
E_STRICT
|
Run-time notices. Enable to have PHP suggest changes
to your code which will ensure the best interoperability and forward
compatibility of your code.
|
4096
|
E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR
|
Catchable fatal error. This is like an E_ERROR but can
be caught by a user defined handle (see also set_error_handler())
|
8191
|
E_ALL
|
All errors and warnings, except level E_STRICT
(E_STRICT will be part of E_ALL as of PHP 6.0)
|
All the above error level can be set using following PHP
built-in library function where level cab be any of the value defined in above
table.
int error_reporting ( [int $level] )
|
Following is the way you can create one error handling
function:
<?php
function handleError($errno, $errstr,$error_file,$error_line)
{
echo "<b>Error:</b> [$errno] $errstr - $error_file:$error_line";
echo "<br />";
echo "Terminating PHP Script";
die();
}
?>
|
Once you define your custom error handler you need to
set it using PHP built-in library set_error_handler function. Now lets
examine our example by calling a function which does not exist.
<?php
error_reporting( E_ERROR );
function handleError($errno, $errstr,$error_file,$error_line)
{
echo "<b>Error:</b> [$errno] $errstr - $error_file:$error_line";
echo "<br />";
echo "Terminating PHP Script";
die();
}
//set error handler
set_error_handler("handleError");
//trigger error
myFunction();
?>
|
Exceptions
Handling:
PHP 5 has an exception model similar to that of other
programming languages. Exceptions are important and provides a better control
over error handling.
Lets explain thre new keyword related to exceptions.
·
Try - A function using an exception should be in a
"try" block. If the exception does not trigger, the code will
continue as normal. However if the exception triggers, an exception is
"thrown".
·
Throw - This is how you trigger an
exception. Each "throw" must have at least one "catch".
·
Catch - - A "catch" block
retrieves an exception and creates an object containing the exception
information.
When an exception is thrown, code following the
statement will not be executed, and PHP will attempt to find the first matching
catch block. If an exception is not caught, a PHP Fatal Error will be issued
with an "Uncaught Exception ...
·
An exception can be thrown, and caught
("catched") within PHP. Code may be surrounded in a try block.
·
Each try must have at least one corresponding catch
block. Multiple catch blocks can be used to catch different classes of
exeptions.
·
Exceptions can be thrown (or re-thrown) within a catch
block.
Example:
Following is the piece of code, copy and paste this code
into a file and verify the result.
<?php
try {
$error = 'Always throw this error';
throw new Exception($error);
// Code following an exception is not executed.
echo 'Never executed';
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "\n";
}
// Continue execution
echo 'Hello World';
?>
|
In the above example $e->getMessage function is uded
to get error message. There are following functions which can be used from Exception
class.
·
getMessage()- message of exception
·
getCode() - code of exception
·
getFile() - source filename
·
getLine() - source line
·
getTrace() - n array of the backtrace()
·
getTraceAsString() - formated string of trace
Creating
Custom Exception Handler:
You can define your own custome excpetion handler. Use
following function to set a user-defined exception handler function.
string set_exception_handler ( callback $exception_handler )
|
Here exception_handler is the name of the
function to be called when an uncaught exception occurs. This function must be
defined before calling set_exception_handler().
Example:
<?php
function exception_handler($exception) {
echo "Uncaught exception: " , $exception->getMessage(), "\n";
}
set_exception_handler('exception_handler');
throw new Exception('Uncaught Exception');
echo "Not Executed\n";
?>
|
Check complete set of error handling functions at PHP
Error Handling Functions
==========================================================================================================
<?php/* Execute a prepared statement by binding PHP variables */$calories = 150;$colour = 'red';$sth = $dbh->prepare('SELECT name, colour, calories
FROM fruit
WHERE calories < ? AND colour = ?');$sth->bindValue(1, $calories, PDO::PARAM_INT);$sth->bindValue(2, $colour, PDO::PARAM_STR);$sth->execute();?>
==========================================================================================================
Source http://php.net/manual/en/filter.filters.sanitize.php
==========================================================================================================
==========================================================================================================
PDO::PARAM_BOOL (integer)
Represents a boolean data type.
PDO::PARAM_NULL (integer)
Represents the SQL NULL data type.
PDO::PARAM_INT (integer)
Represents the SQL INTEGER data type.
PDO::PARAM_STR (integer)
Represents the SQL CHAR, VARCHAR, or other string data type.
PDO::PARAM_LOB (integer)
Represents the SQL large object data type.
PDO::PARAM_STMT (integer)
Represents a recordset type. Not currently supported by any drivers.
PDO::PARAM_INPUT_OUTPUT (integer)
Specifies that the parameter is an INOUT parameter for a stored procedure. You must bitwise-OR this value with an explicit PDO::PARAM_* data type.<?php/* Execute a prepared statement by binding PHP variables */$calories = 150;$colour = 'red';$sth = $dbh->prepare('SELECT name, colour, calories
FROM fruit
WHERE calories < ? AND colour = ?');$sth->bindValue(1, $calories, PDO::PARAM_INT);$sth->bindValue(2, $colour, PDO::PARAM_STR);$sth->execute();?>
==========================================================================================================
filter_var($_POST['email'], FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL);
Sanitize filters
| ID | Name | Options | Flags | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL | "email" | Remove all characters except letters, digits and !#$%&'*+-/=?^_`{|}~@.[]. | ||
FILTER_SANITIZE_ENCODED | "encoded" | FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_HIGH | URL-encode string, optionally strip or encode special characters. | |
FILTER_SANITIZE_MAGIC_QUOTES | "magic_quotes" | Apply addslashes(). | ||
FILTER_SANITIZE_NUMBER_FLOAT | "number_float" | FILTER_FLAG_ALLOW_FRACTION,FILTER_FLAG_ALLOW_THOUSAND,FILTER_FLAG_ALLOW_SCIENTIFIC | Remove all characters except digits, +- and optionally .,eE. | |
FILTER_SANITIZE_NUMBER_INT | "number_int" | Remove all characters except digits, plus and minus sign. | ||
FILTER_SANITIZE_SPECIAL_CHARS | "special_chars" | FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_HIGH | HTML-escape '"<>& and characters with ASCII value less than 32, optionally strip or encode other special characters. | |
FILTER_SANITIZE_FULL_SPECIAL_CHARS | "full_special_chars" | FILTER_FLAG_NO_ENCODE_QUOTES, | Equivalent to callinghtmlspecialchars() withENT_QUOTES set. Encoding quotes can be disabled by settingFILTER_FLAG_NO_ENCODE_QUOTES. Like htmlspecialchars(), this filter is aware of thedefault_charset and if a sequence of bytes is detected that makes up an invalid character in the current character set then the entire string is rejected resulting in a 0-length string. When using this filter as a default filter, see the warning below about setting the default flags to 0. | |
FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING | "string" | FILTER_FLAG_NO_ENCODE_QUOTES,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_AMP | Strip tags, optionally strip or encode special characters. | |
FILTER_SANITIZE_STRIPPED | "stripped" | Alias of "string" filter. | ||
FILTER_SANITIZE_URL | "url" | Remove all characters except letters, digits and $-_.+!*'(),{}|\\^~[]`<>#%";/?:@&=. | ||
FILTER_UNSAFE_RAW | "unsafe_raw" | FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_LOW,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_HIGH,FILTER_FLAG_ENCODE_AMP | Do nothing, optionally strip or encode special characters. |
==========================================================================================================
Go to command prompt, cd to the appropriate folder and type:
notepad .htaccess After confirmation dialog the file will be created and you will be editing it directly. If you just want to create an empty file, try
echo. > .htaccessorcreate the file by typing ".htaccess." in explorer, and the last dot will be removed automatically.
- Create a Web page that will be your 404 document.
- Open yourhttpd.conffile for editing (you'll probably have to login as root to edit it).
- Find the line that reads
ErrorDocument 404 /404.html - Change the third entry to the URI you would like to display, e.g.
ErrorDocument 404 /new_404.html
Exception::getCode
(PHP 5 >= 5.1.0)Exception::getCode — Gets the Exception code
<?phptry {throw new Exception("Some
error message", 30);} catch(Exception $e) {echo "The exception code is: " . $e->getCode();}?>This document will explain how to create a .htaccess file to redirect your site or site content. This will not redirect any emails for your domains.
READ ME FIRST
As a configuration file,
Since
This article is provided as a courtesy. Installing, configuring, and troubleshooting third-party applications is outside the scope of support provided by (mt) Media Temple. Please take a moment to review the Statement of Support.
As a configuration file,
.htaccess is very powerful. Even the slightest syntax error (like a missing space) can result in your content not displaying correctly or at all. Since
.htaccess is a hidden system file, please make sure your FTP client is configured to show hidden files. This is usually an option in the program's preferences/options. This article is provided as a courtesy. Installing, configuring, and troubleshooting third-party applications is outside the scope of support provided by (mt) Media Temple. Please take a moment to review the Statement of Support.
Instructions
NOTE:
The reason you should save the file as htaccess.txt is because many operating systems and FTP applications are unable to read or view
2. Edit the contents of the file. Check the following examples: The reason you should save the file as htaccess.txt is because many operating systems and FTP applications are unable to read or view
.htaccess files by default. Once uploaded to the server you can rename the file to .htaccess. 301 (Permanent) Redirect: Point an entire site to a different URL on a permanent basis. This is the most common type of redirect and is useful in most situations. In this example, we are redirecting to the "mt-example.com" domain:
# This allows you to redirect your entire website to any other domain
Redirect 301 / http://mt-example.com/
# This allows you to redirect your entire website to any other domain
Redirect 302 / http://mt-example.com/
# This allows you to redirect index.html to a specific subfolder
Redirect /index.html http://example.com/newdirectory/
# Redirect old file path to new file path
Redirect /olddirectory/oldfile.html http://example.com/newdirectory/newfile.html# Provide Specific Index Page (Set the default handler)
DirectoryIndex index.html
.htaccess.
NOTE:
- If using a text editor, be sure to save the file as plain text.
- Paths to where you should save this file can be found in this article: System paths.
- The definitive guide on Apache directives that can be used in .htaccess files can be found here: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/mod/core.html.
More powerful URL changes with mod_rewrite
If you need to make complex changes to the way your URL displays, you should visit Using .htaccess rewrite rules. You can do things like add "www" to the beginning of your URL, redirect all requests to a subfolder but keep the rest of the URL, etc.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Here’s a very simple solution to handling a variety of HTTP errors like 404, 500.. etc in one php file. All we need to do is create an array of error codes and match against them by picking up the global redirect status code using PHP. This means that we can use one page the handle multiple errors.
Here’s a very simple solution to handling a variety of HTTP errors like 404, 500.. etc in one php file. All we need to do is create an array of error codes and match against them by picking up the global redirect status code using PHP. This means that we can use one page the handle multiple errors.
The Code
You’ll need
to update your .htaccess file so when an error is detected the server knows how
to handle the request. In our case we’re going to forward all the listed errors
to our generic errors.php file.
ErrorDocument 400 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 403 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 404 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 405 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 408 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 500 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 502 /errors.php
ErrorDocument 504 /errors.php
The PHP
This is the
contents of the ‘errors.php’ file. You need to save this in the root directory
of your web server, unless you modify the path in the .htaccess file above.
$status =
$_SERVER['REDIRECT_STATUS'];$codes = array(400 => array('400 Bad
Request', 'The request cannot be fulfilled due to bad syntax.'),403 => array('403
Forbidden', 'The server has refused to fulfil your request.'),404 => array('404 Not
Found', 'The page you requested was not found on this server.'),405 => array('405 Method
Not Allowed', 'The method specified in the request is not allowed for the
specified resource.'),408 => array('408 Request
Timeout', 'Your browser failed to send a request in the time allowed by the
server.'),500 => array('500 Internal
Server Error', 'The request was unsuccessful due to an unexpected condition
encountered by the server.'),502 => array('502 Bad
Gateway', 'The server received an invalid response while trying to carry out
the request.'),504 => array('504 Gateway
Timeout', 'The upstream server failed to send a request in the time allowed
by the server.'),); |
||
|
if ($title == false || strlen($status) != 3) { |
$message = 'Please supply a valid HTTP status code.'; |
=======================================================================
PHP Try and Catch for SQL Insert
You can implement throwing exceptions on mysql query fail on your own. What you need is to write a wrapper for mysql_query function, e.g.:
// user defined. corresponding MySQL errno for duplicate key entry
const MYSQL_DUPLICATE_KEY_ENTRY = 1022;
// user defined MySQL exceptions
class MySQLException extends Exception {}
class MySQLDuplicateKeyException extends MySQLException {}
function my_mysql_query($query, $conn=false) {
$res = mysql_query($query, $conn);
if (!$res) {
$errno = mysql_errno($conn);
$error = mysql_error($conn);
switch ($errno) {
case MYSQL_DUPLICATE_KEY_ENTRY:
throw new MySQLDuplicateKeyException($error, $errno);
break;
default:
throw MySQLException($error, $errno);
break;
}
}
// ...
// doing something
// ...
if ($something_is_wrong) {
throw new Exception("Logic exception while performing query result processing");
}
}
try {
mysql_query("INSERT INTO redirects SET ua_string = '$ua_string'")
}
catch (MySQLDuplicateKeyException $e) {
// duplicate entry exception
$e->getMessage();
}
catch (MySQLException $e) {
// other mysql exception (not duplicate key entry)
$e->getMessage();
}
catch (Exception $e) {
// not a MySQL exception
$e->getMessage();
}http://www.php.net/manual/en/language.exceptions.php
http://papermashup.com/create-an-error-page-to-handle-all-errors-with-php/
http://kb.mediatemple.net/questions/242/How+do+I+redirect+my+site+using+a+.htaccess+file%3F
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1918624/php-try-and-catch-for-sql-insert